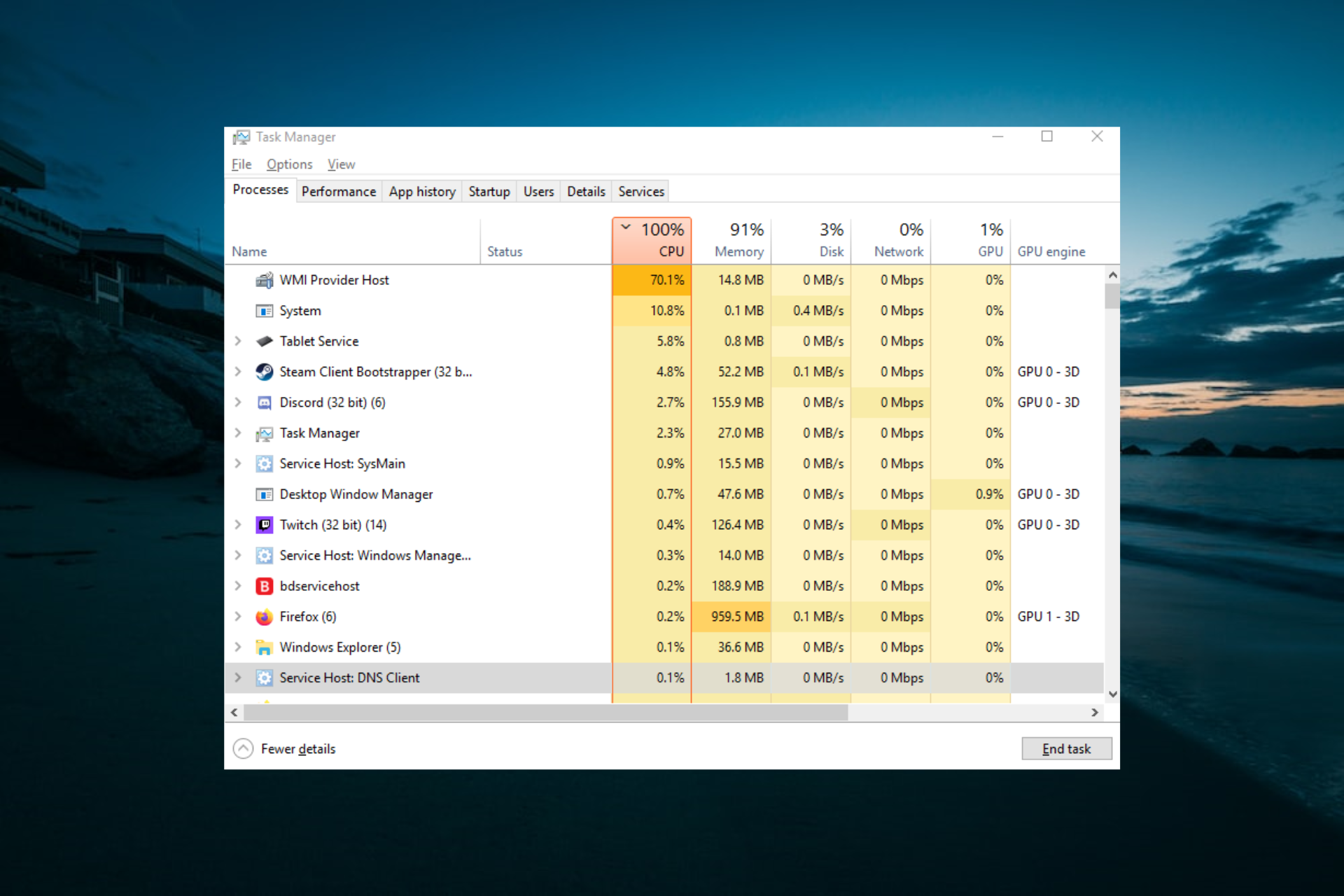
Understanding Wmiprvse High CPU Usage
The * process, part of the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service, handles system monitoring and queries. High CPU usage typically stems from malicious software, corrupted files, or misconfigured tasks. Addressing this requires efficient solutions to restore system performance.
5 Quick Solutions to Resolve Wmiprvse High CPU Usage
Implement these steps sequentially for optimal results. Always run tools with administrative privileges.
- Run a Full Malware Scan
Use Windows Security or a trusted third-party antivirus to detect and remove threats. Malware often exploits WMI services, causing excessive CPU load. Perform a comprehensive scan and follow recommended actions.

- Install All Windows Updates
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and install pending updates. Outdated components can trigger wmiprvse issues; updates patch vulnerabilities and optimize performance.
- Restart the WMI Service
Open the Services app (*), locate Windows Management Instrumentation, right-click to stop it, wait a moment, then restart it. This clears temporary glitches without system-wide reboots.
- Perform a System File Check
Launch Command Prompt as administrator and execute sfc /scannow. This tool repairs corrupted Windows files that may disrupt WMI functionality, resolving underlying CPU spikes.
- Analyze Event Viewer Logs
Search Event Viewer > Windows Logs > Application for WMI-related errors (e.g., event ID 10 or 1001). Investigate details to pinpoint problematic tasks or scripts and disable or reconfigure them manually.
Key Considerations
If issues persist after trying all steps, consider backing up data and resetting Windows. Avoid unnecessary registry edits, as they can worsen performance. Monitor CPU usage regularly through Task Manager to confirm resolution.