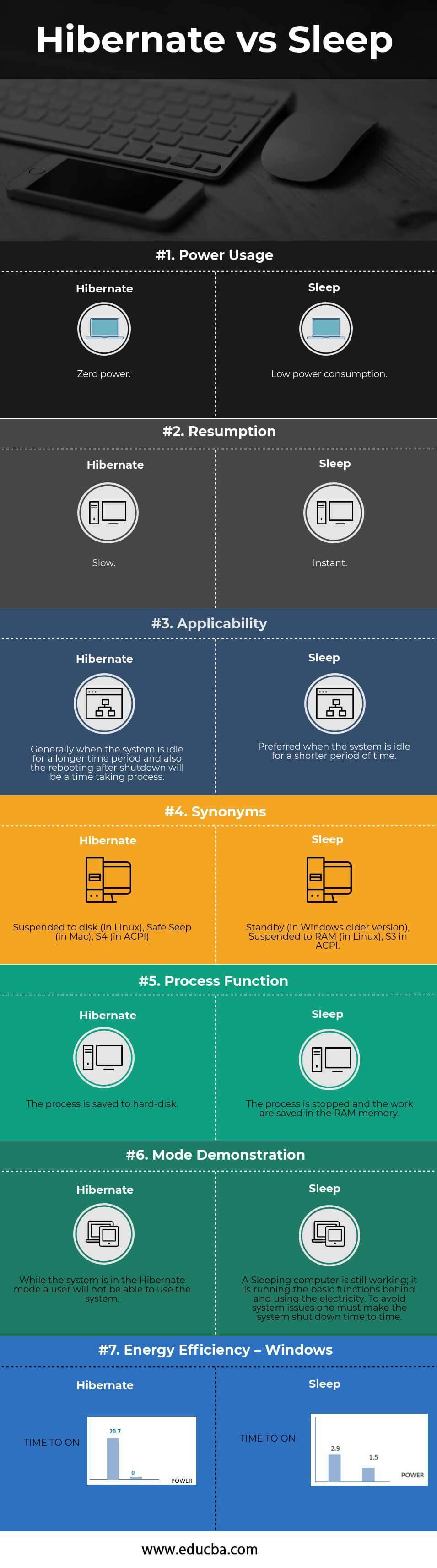
Understanding Windows power states optimizes device usage. Below compares Sleep and Hibernate mechanics, activation, and best use cases.
Technical Mechanism Comparison
Sleep (Standby):
- Powers down display, CPU, and non-essential hardware components.
- Maintains active low-power state in RAM.
- Requires continuous minimal power source (battery or AC).
- Data resides exclusively in volatile RAM.
Hibernate:

- Saves complete RAM state (open apps/files) to disk (*).
- Performs full system shutdown after saving RAM image.
- Uses zero power once hibernation completes.
- Data persists on non-volatile storage.
Activation & Resumption Steps
Entering Sleep:
- Select Power Button in Start Menu.
- Choose "Sleep".
- Device enters low-power state within seconds.
Resuming from Sleep:
- Press keyboard key or power button.
- System wakes instantly (1-3 seconds).
- All applications/files remain exactly as left.
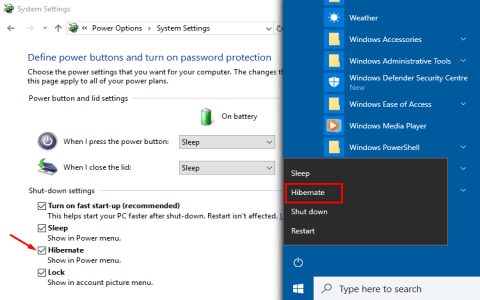
Entering Hibernate (if enabled):
- Open Settings > System > Power & Sleep.
- Click "Additional Power Settings".
- Select "Choose what the power button does".
- Click "Change settings currently unavailable".
- Check "Hibernate" under Shutdown settings.
- Select Power Button > Hibernate.
Resuming from Hibernate:
- Press power button.
- System boots normally but loads saved RAM state.
- Resumes to previous state in 15-45 seconds (depends on SSD/HDD speed).
Scenario Recommendations
Use Sleep When:
- Taking short breaks (minutes to hours).
- Requiring near-instant resumption.
- Connected to reliable power (prevent data loss on battery drain).
Use Hibernate When:
- Pausing work for extended periods (overnight/travel).
- Critical to preserve battery life.
- Uncertain about power availability.
- Prefer safe shutdown with session restore capabilities.
Hybrid Sleep (Desktop Focus): Combines Sleep and Hibernate by saving RAM to disk while keeping RAM powered. Protects against power failure during Sleep.