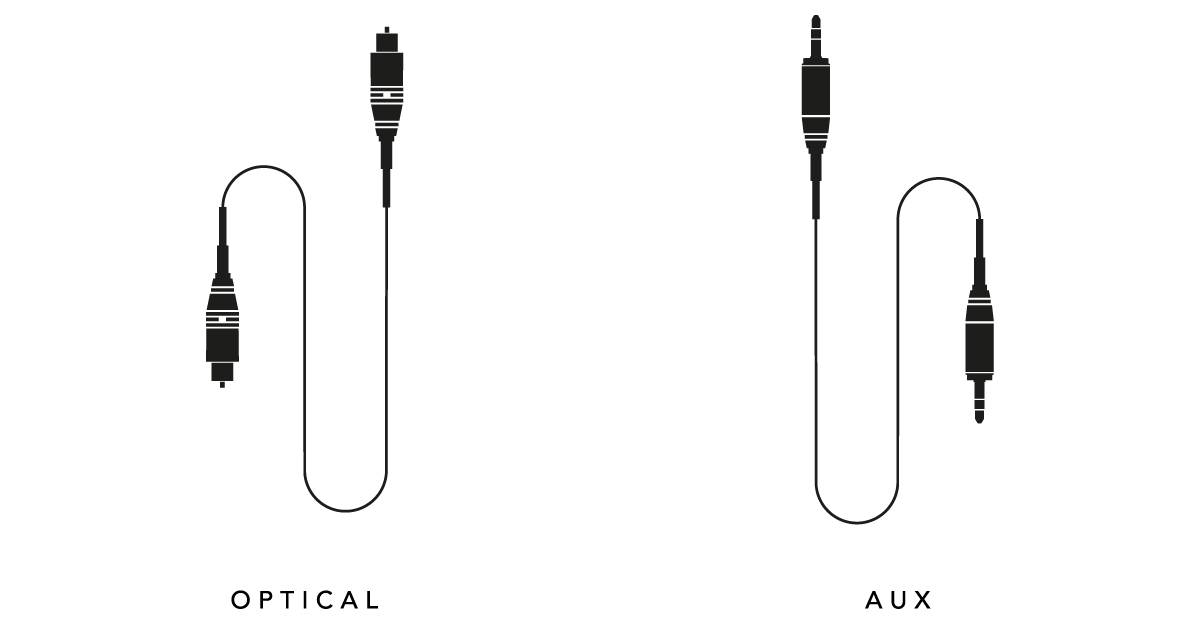
Optical audio, technically known as TOSLINK (Toshiba Link), is a standardized interface for transmitting digital audio signals between devices using pulses of light transmitted through a fiber optic cable with a core diameter of approximately 1mm. Unlike analog connections using electrical currents, optical audio carries digital data.
Key Advantages of Optical Audio Over Analog Sound
Optical transmission fundamentally differs from analog audio cables, offering distinct benefits:
- Immunity to Electrical Interference (EMI/RFI): As light pulses travel through a fiber optic cable, they are completely impervious to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This prevents the hums, buzzes, or degraded sound quality often introduced by nearby power cables, motors, Wi-Fi routers, or fluorescent lighting that plague analog connections.
- Prevents Ground Loops: Because fiber optics carry light, not electricity, they physically isolate the grounding circuits of connected devices. This eliminates ground loop hum, a persistent and troublesome low-frequency buzz common in analog setups when interconnected devices have slightly different electrical ground potentials.
- Perfect Channel Isolation: Digital transmission ensures the absolute separation of audio channels. There is zero crosstalk between channels (like Left and Right), preserving the intended stereo image or surround soundfield, which can degrade slightly in analog systems, especially over longer cable runs.
- High Fidelity Potential: Optical audio can transmit uncompressed high-resolution stereo (LPCM) audio formats (up to 24-bit/192kHz) and compressed multi-channel formats like Dolby Digital and DTS used in home theater. It transmits the original digital signal without the inherent signal degradation, capacitance, and resistance losses that occur as analog electrical signals travel through wire.
- Longer Distance Capability: While analog audio signals lose quality over distance due to resistance and interference, optical cables maintain signal integrity over longer distances without degradation, typically up to 10 meters effectively (and further with higher-quality fibers).
In essence, optical audio provides a clean conduit for digital audio signals, offering superior clarity and reliability by eliminating the primary weaknesses of analog electrical transmission – interference and ground loops – making it the preferred choice for high-fidelity audio and sophisticated audio setups.