5G+, often referred to as 5G Advanced or 5G+, signifies a significant evolution beyond foundational 5G (often called 5G Non-Standalone or NSA). It leverages enhanced technologies and spectrum utilization to deliver substantially improved performance and capabilities.
Core Technologies Enabling 5G+
- Aggressive Carrier Aggregation (CA): Combining more channels of spectrum across low-band (Sub-1 GHz), mid-band (1-6 GHz), and high-band (mmWave, 24 GHz+) frequencies simultaneously.
- Advanced Massive MIMO: Utilizing larger antenna arrays and more sophisticated beamforming techniques for increased capacity and coverage.
- Higher-Order Modulation (e.g., 1024-QAM): Packing more data bits into each radio signal transmission.
- mmWave Expansion: Broader deployment of ultra-high-frequency mmWave spectrum in dense urban areas and venues.
- Network Slicing: Creating virtualized, dedicated network segments with guaranteed performance for specific applications.
- Cloud-Native Core & Edge Computing: Enhanced network architecture enabling lower latency and localized processing.
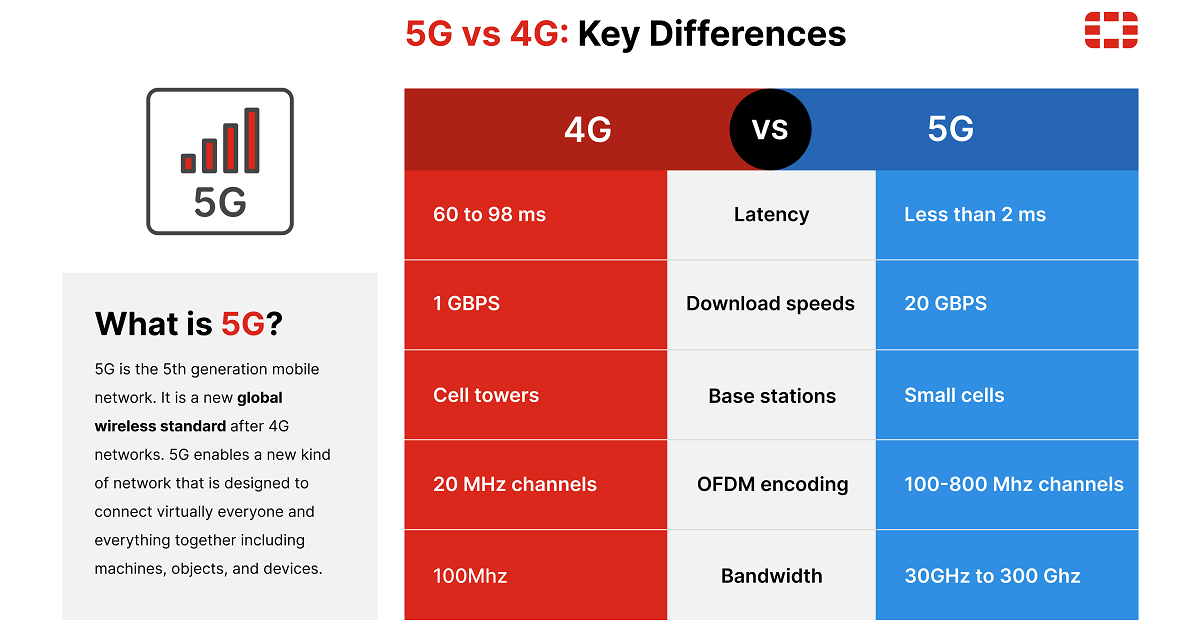
Performance Comparison: 5G+ vs. Regular 5G
The technological advancements translate into tangible performance gains:
- Peak & Real-World Speeds: Significantly higher peak speeds (multi-Gigabit range) and greatly improved sustained speeds, especially in challenging conditions. Regular 5G (especially on low/mid-band) can be susceptible to congestion slowdowns.
- Latency: Reduced latency, approaching single-digit milliseconds. This is crucial for real-time applications like cloud gaming, industrial automation, and XR.
- Capacity & Density: Superior ability to handle many more simultaneous connections in congested areas (stadiums, city centers) without performance degradation.
- Reliability & Consistency: More stable connections with less variability in speed and latency, providing a predictable experience. Regular 5G coverage can be patchy, particularly indoors, relying heavily on lower bands.
- Coverage Type: While regular 5G often relies predominantly on low-band and some mid-band, 5G+ heavily leverages mid-band (especially C-band) and strategically deploys mmWave for extreme hotspot capacity.
Deployment & Use Cases
5G+ is primarily deployed in high-demand urban centers, enterprise campuses, and venues needing massive capacity and ultra-low latency. It powers advanced use cases:
- Immersive XR (AR/VR/XR)
- Reliable industrial IoT automation and control
- Mission-critical services requiring guaranteed network slices
- Massive-scale high-definition live streaming
- Evolution towards 6G foundations.
Regular 5G provides the foundational coverage layer, improving upon 4G LTE but often lacking the consistent high performance of 5G+. It handles standard broadband replacement and consumer mobile broadband effectively.
Key Differentiation Summary:
| Feature | Regular 5G | 5G+ |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Focus | Basic CA, Some MIMO | Advanced CA (incl mmWave), Massive MIMO, Higher QAM |
| Speed Consistency | Variable, slows under load | Much more consistent, sustains high speeds |
| Peak Speeds | Gigabit range | Multi-Gigabit range |
| Latency | Lower than 4G (~30-50ms) | Ultra-Low (~10ms or less) |
| Capacity/Density | Moderate improvement over 4G | Significant leap, handles extreme density |
| Primary Spectrum | Low-band (nationwide), some Mid-band | Dense Mid-band (e.g., C-band), Targeted mmWave |
| Target Use Cases | Enhanced Mobile Broadband | Advanced Apps (XR, IoT Automation), Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) |
| Deployment Area | Broad Coverage | Focused: Dense Urban, Venues, Enterprise |