Renaming directories in Linux via the terminal uses the mv command. This tool moves or renames files and directories when source and target reside on the same filesystem.
Basic Syntax
The command structure is:
mv [OPTIONS]
Replace source_directory with the original directory name and target_directory with the new name.
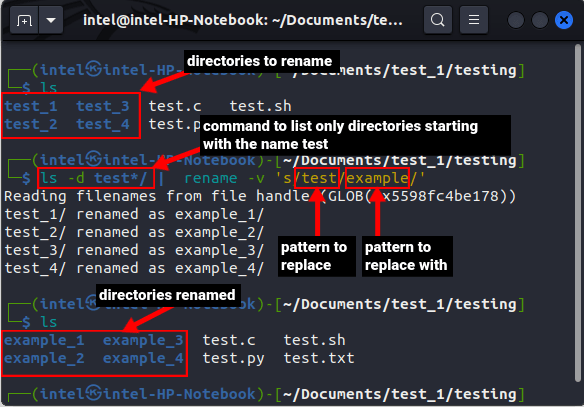
Step-by-Step Guide
- Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T or equivalent).
- Navigate to the parent directory containing the target folder using cd.
- Execute the mv command with appropriate names.
Practical Examples
Example 1: Rename "Documents" to "Docs"
mv Documents Docs
Verity with ls to confirm the change.
Example 2: Rename a directory with spaces (use quotes or escape spaces)
mv "Old Project" New_Project # Using quotes
or
mv Old Project New_Project # Escaping spaces with backslashes
Example 3: Rename a directory in a different path (absolute paths)
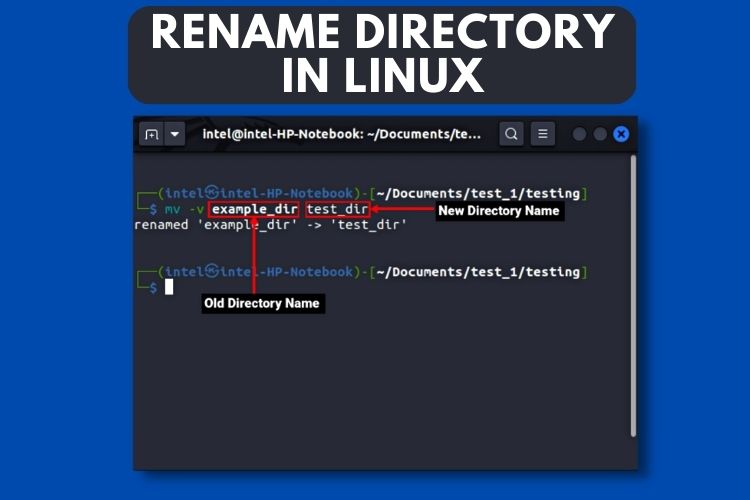
mv /home/user/Downloads/temp /home/user/Downloads/archive
Critical Notes
- The mv command overwrites existing directories with the same name by default. Use mv -i for interactive confirmation before overwriting.
- Requires write permissions in the parent directory. Prefix commands with sudo if ownership restrictions exist (e.g., sudo mv dir1 dir2).
- Renaming directories preserves all contents and metadata (permissions, timestamps).
For verbose output showing renamed paths, add the -v flag (e.g., mv -v Folder1 Folder2).