Introduction to Adding Scripts as Desktop Apps
Adding a script as a desktop application simplifies launching from your Linux menu. This guide covers steps for common desktops like GNOME or KDE using .desktop files.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Create a .desktop file in a text editor (e.g., nano).
- Insert this template, adjusting paths:
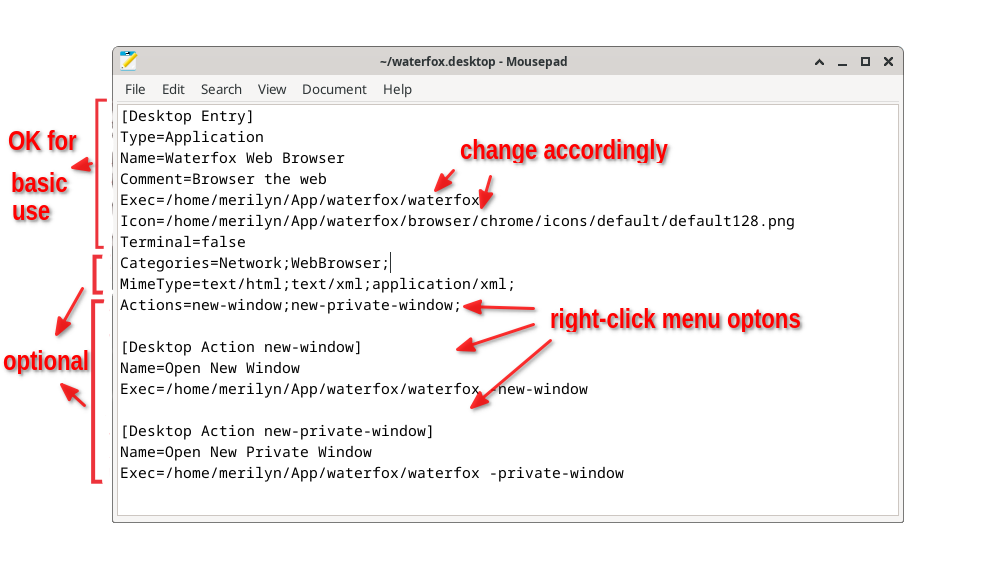
[Desktop Entry]
Name=MyScript
Exec=/path/to/*
Icon=/path/to/*
Terminal=false
Type=Application - Save the file with a .desktop extension, such as *.
- Place the file in ~/.local/share/applications for user-level access.
- Set executable permissions via terminal: chmod +x /path/to/*.
- Log out or restart to refresh the application menu.
Verification and Customization
After completion, search for the app name in your desktop menu. Customize fields like Terminal=true to run scripts requiring a console. Ensure script paths are absolute for reliability.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Verify .desktop syntax with desktop-file-validate command.
- Test script execution permissions independently.
- Use generic icons if custom ones are unavailable.