Identifying your laptop's GPU is essential for driver updates, troubleshooting, or checking game/system requirements. Here are efficient methods:
For Windows Users
Using Device Manager:
- Press Win + X and select "Device Manager".
- Expand the "Display adapters" section.
- Your primary graphics card(s) will be listed (e.g., NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050, AMD Radeon RX 6700S, or Intel Iris Xe Graphics).
Using DirectX Diagnostic Tool:
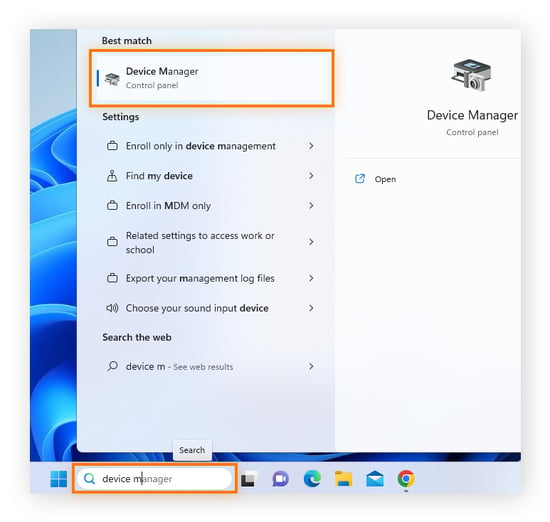
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type "dxdiag" and press Enter.
- Click the "Display" tab.
- The "Name" field shows your active GPU model. Check all Display tabs if multiple GPUs exist.
For macOS Users
- Click the Apple menu () and select "About This Mac".
- Look under "Chip" or "Graphics" in the Overview tab for your GPU (e.g., "Apple M2 Pro", "AMD Radeon Pro 5500M").
Important Considerations
- Modern laptops often use hybrid graphics (integrated + dedicated). Tools show both; the dedicated GPU (NVIDIA/AMD) handles intensive tasks.
- Windows Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc > Performance tab) shows real-time GPU usage by name.
- Laptop GPUs typically have "M", "Max-Q", or "Mobile" in naming conventions, differing from desktop counterparts.