Essential Equipment and Setup
Digitizing cassette tapes to digital files preserves audio without expensive tools. Start with a functional cassette player or deck, as this is often the most costly item but can be sourced secondhand or borrowed.
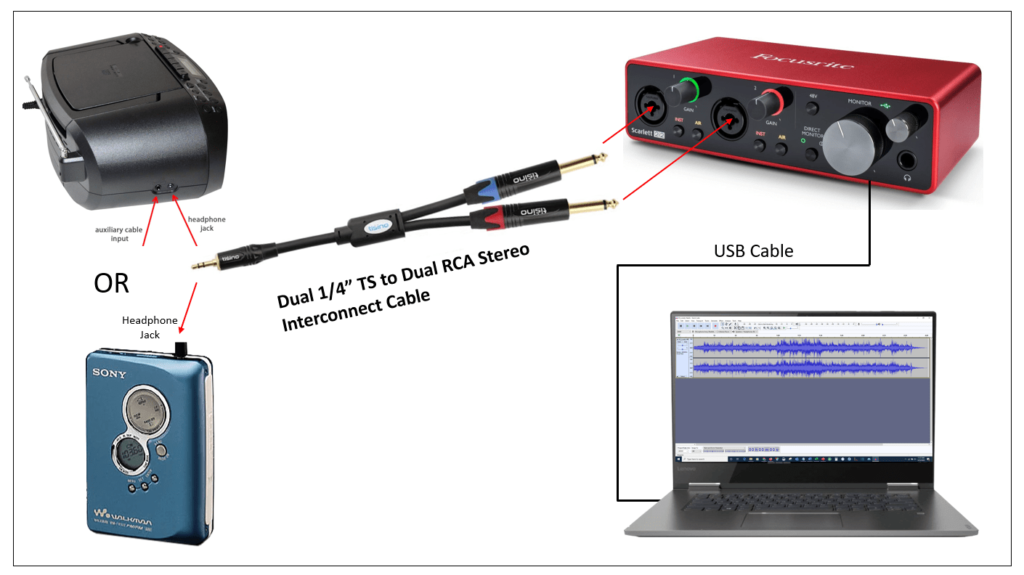
Method 1: Computer and Audio Cable Connection
This approach uses existing computer components for minimal cost. Connect the cassette player's headphone output to your computer's line-in or microphone port using a basic 3.5mm audio cable. Avoid adapters to reduce noise.
Steps:

- Set your computer's audio input to "Line-in" via sound settings.
- Use free software like Audacity to record: set sample rate to 44.1kHz and format to WAV for quality.
- Press play on the cassette and start recording; pause between tracks for easy splitting later.
Tip: Keep the cassette player away from electrical interference for cleaner audio.
Method 2: USB Cassette Converter Devices
Affordable USB digitizers (often under $20) plug directly into computers, simplifying the process without cables. Ensure compatibility with your operating system before purchase.
Steps:
- Insert the cassette into the converter and connect to a USB port.
- Use included software or Audacity to record; set output to MP3 for compact files.
- Monitor levels to prevent distortion—adjust gain if needed.
Tip: Clean cassette heads before use to avoid audio degradation.
Method 3: Smartphone with Audio Jack or Adapter
Modern smartphones can digitize tapes if they have a headphone jack or via a cheap adapter. This leverages free apps for on-the-go archiving.

Steps:
- Connect the cassette player to the phone's headphone jack with a 3.5mm cable; for jacks, use a TRRS adapter.
- Install a recording app like Voice Recorder & Audio Editor; choose high-quality settings.
- Record in a quiet room to minimize background noise, and trim files afterward.
Tip: Test with a short tape first to fine-tune levels and positioning.
Quality Optimization Tips
Ensure digital files sound crisp:
- Clean the cassette player regularly with isopropyl alcohol to remove dust.
- Normalize audio levels post-recording using software tools.
- Store files in multiple formats (e.g., WAV for archives, MP3 for everyday use).
Avoid playing worn tapes repeatedly; digitize once to preserve originals.