Creating Symbolic Links on Mac via Terminal
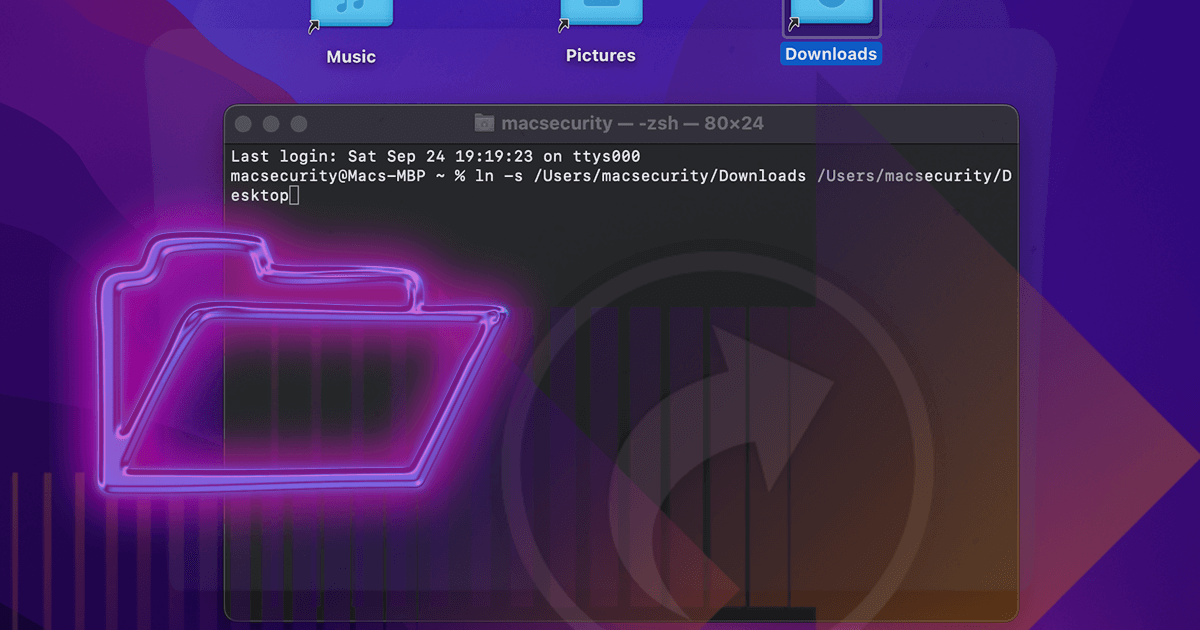
A symbolic link (symlink) acts as a pointer to another file or directory, offering flexibility without duplicating data. Use the ln command in Terminal for reliable creation.
Essential Command Syntax
- The core command is: ln -s <source_path> <link_path>
- -s specifies symbolic linking.
- <source_path>: Full path to the original file or folder.
- <link_path>: Path and name for the new symlink.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Open Terminal: Launch Terminal from Applications → Utilities or via Spotlight (Cmd + Space, then type "Terminal").
- Execute the Command: Type ln -s <source_path> <link_path> and press Enter. For example:
Example: To link a file "*" to a desktop shortcut: ln -s /Users/you/Documents/* /Users/you/Desktop/shortcut
Best Practices
- Prefer absolute paths (e.g., /Users/...) over relative paths to avoid broken links.
- Verify links with ls -l <link_path> to see the target reference.
- Delete symlinks using rm <link_path> without affecting the source.
Regularly check permissions with ls -la to ensure access; errors often arise from incorrect paths or limited write privileges.