Understanding Symbolic Links
A symbolic link (symlink) acts as a pointer to another file or directory on your Mac OS. It saves space, avoids duplication, and maintains updates across locations.
Steps to Create a Symlink Using Terminal
This method uses Terminal for precise control:
- Step 1: Launch Terminal (find it in Applications > Utilities or use Spotlight).
- Step 2: Navigate to the desired directory. Use cd /path/to/directory to change locations.
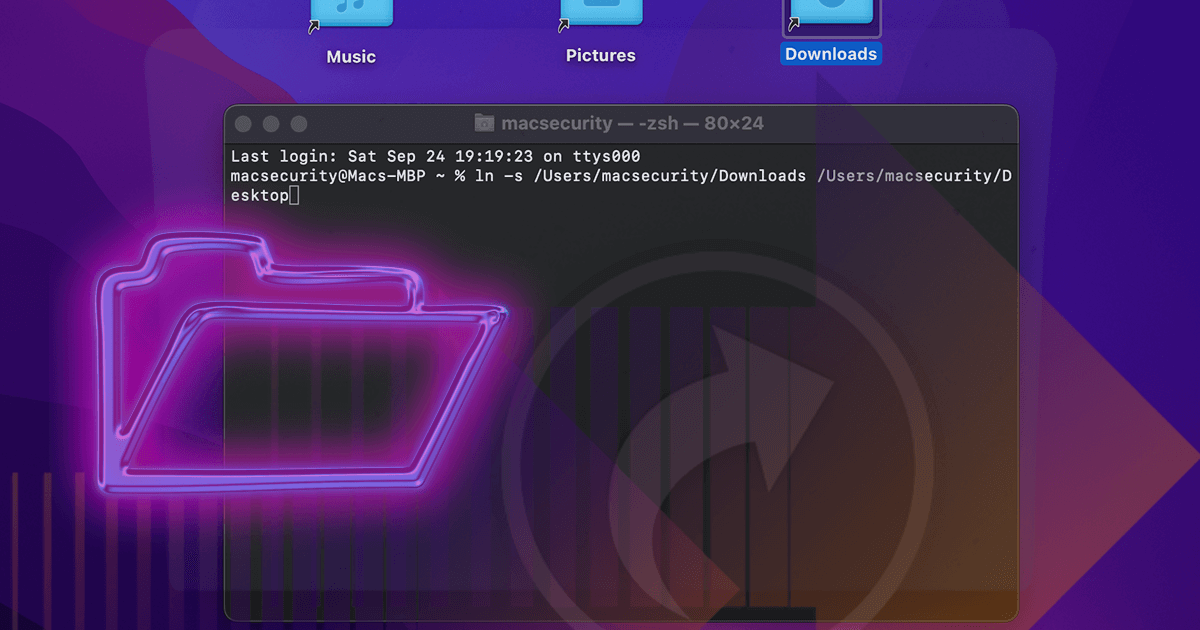
- Step 3: Execute the command. Type ln -s /source/path link_name. Replace /source/path with the file/directory to reference, and link_name with the symlink's name.
- Step 4: Verify the symlink. Use ls -l to list contents. The output shows link_name -> /source/path for confirmation.
Common Tips and Troubleshooting
Use absolute paths for reliability to avoid broken links. For directories, add a trailing slash if needed. If issues arise, run man ln in Terminal for manual guidance.