Variable assignment is fundamental in Bash scripting. Here are key methods and rules:
Basic Variable Assignment
Use the operator with no spaces:
name="value"
count=5
Accessing Variables
Prefix the variable name with :
echo $name # Outputs 'value'
result=$((count 2))
Key Rules
- No spaces around :
var=42works;var = 42fails - Variable names are case-sensitive:
$Varand$vardiffer - Use uppercase by convention:
API_KEY="secret" - Names can contain letters, numbers, underscores:
user_1="Alice"
Quoting Values
Use double quotes for multi-word values:
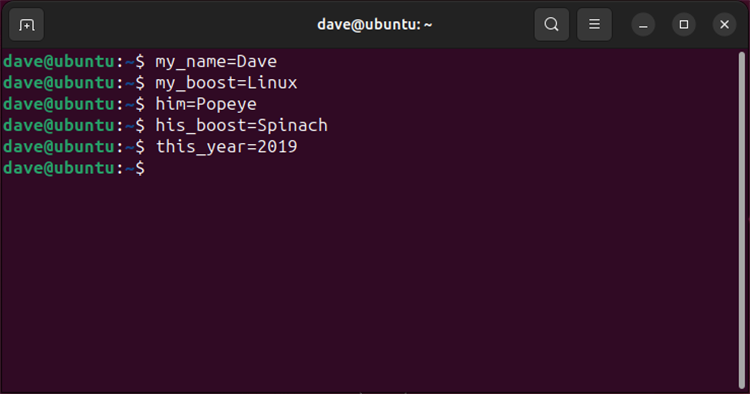
message="Hello World"
path="/home/user/docs"
Prevent unexpected word splitting with special characters using quotes.
Assigning Command Output
Capture command output with or backticks:
current_date=$(date)
file_list=`ls /dir`
Read-only Variables
Declare constants with readonly:
readonly MAX_CONNECTIONS=10
Local Variables in Functions
Limit scope with local:
myfunc() {
local func_var="This exists only in myfunc"
Advanced Assignment Techniques
- Default value:
${var:-default} - Assignment with default:
${var:=backup_value} - Declare integer:
declare -i num=5 - Associative arrays:
declare -A dict=(["key"]="value")
Practice these patterns to build robust scripts while avoiding common syntax pitfalls.