A BIOS Version Checker Tool identifies the current firmware version running on your computer's motherboard. Understanding and using such a tool correctly is crucial for system stability and security.
Why Check Your BIOS Version?
Verifying your BIOS version serves several critical purposes:
- Compatibility: Latest hardware components (CPUs, RAM, storage) often require an updated BIOS for proper recognition and functionality.
- Security Patches: Vendors frequently release BIOS updates to address critical vulnerabilities discovered post-launch. An outdated BIOS can be an entry point for exploits.
- Bug Fixes and Stability: Updates resolve system instability issues, boot failures, or unexpected behavior stemming from BIOS bugs.
- Performance Optimizations: Some updates improve power management or enhance processing efficiency, potentially boosting system performance.
- Feature Enablement: New firmware might unlock advanced settings or support technologies not present in the original version.
How to Check Your BIOS Version
Several reliable methods exist:
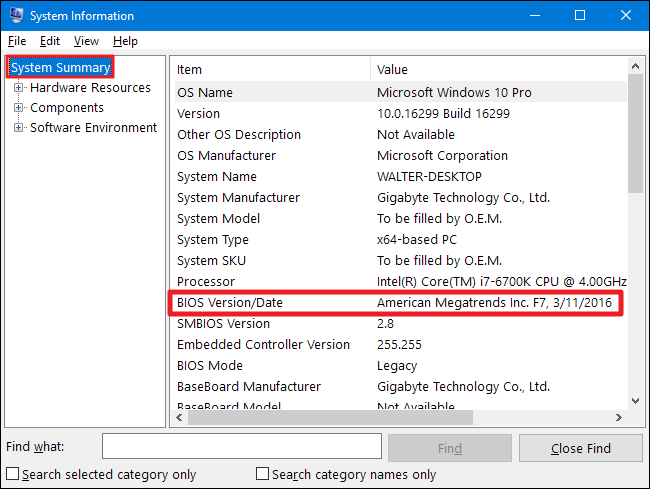
- System Information: Press `Win + R`, type `msinfo32`, and press Enter. Locate "BIOS Version/Date" in the System Summary.
- Command Prompt: Open Command Prompt or PowerShell. Enter `wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion`. The version number will be displayed.
- BIOS Setup Utility: Reboot your PC and enter the BIOS/UEFI setup (typically by pressing F2, Del, or Esc during boot). The version number is usually visible on the main screen.
- OEM Tools: Some manufacturers (Dell, Lenovo, HP, ASUS, etc.) provide system management applications displaying BIOS info.
- Third-Party Software: Specialized system info tools like CPU-Z also list the BIOS version under the "Mainboard" tab.
Using a BIOS Version Checker Safely
Checking the version poses little risk. However, proceed with extreme caution if updating:
- Verify Update Need: Only update if a newer version addresses a specific issue affecting your system or provides critical security fixes. "If it ain't broke, don't fix it" often applies to BIOS updates.
- Source Authentically: Always download BIOS updates directly from your motherboard or system manufacturer's official support website. Never use files from third-party sites or tools.
- Confirm Correct Version: Meticulously match the BIOS file to your exact motherboard model number and current revision. Flashing incorrect firmware is disastrous.
- Power Stability is Critical: Connect your laptop to its charger. For desktops, use a reliable UPS. A power interruption during flashing will brick the motherboard.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Different OEMs utilize different update utilities (Windows-based, bootable USB, within BIOS itself). Strictly adhere to their documented procedure.
- Beware Beta Versions: Avoid beta BIOS unless you are troubleshooting a specific problem documented in the beta release notes. They are less stable.
- Do Not Interrupt: Never reboot, shut down, or disconnect power during the update process. Wait for the utility to complete fully and restart the system automatically.
Regularly checking your BIOS version is a simple yet vital part of system maintenance and security. While updating carries inherent risks, following strict safety protocols minimizes these dangers and ensures your system benefits from necessary improvements and protections.