Renaming directories in Linux is straightforward using the command line. Follow these efficient methods:
Method 1: Using the `mv` Command
The primary tool for renaming directories:
Basic Syntax:

mv old_directory_name new_directory_name
Example Steps:
- 1. Open a terminal
- 2. Navigate to the parent directory containing the target:
cd /path/to/parent - 3. Execute:
mv Projects Project_Backup_2024
Key Flags:
-v: Verbose output (confirms action)-i: Interactive mode (prompts before overwrite)
Method 2: Handling Spaces & Special Characters
Escape spaces or use quotes:
- Escape:
mv Old Name New Name - Single quotes:
mv 'Old Name' 'New Name' - Double quotes:
mv "Old Name" "New Name"
Method 3: Rename Directory In-Place
Specify full paths without changing working directory:
mv /home/user/docs/archive /home/user/docs/historical
Method 4: Using `rename` Command (Bulk Renaming)
For pattern-based renaming (Perl regex):
- Basic syntax:
rename 's/oldpattern/newpattern/' directory_ - Example:
rename 's/photo/img/' img_(Changes "photo001" to "img001")
Method 5: Using `find` with `exec`
Rename directories recursively:
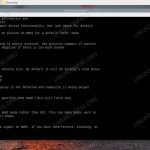
find . -depth -type d -name "oldname" -execdir mv {} newname ;
Critical Tips for Success
- Verify paths: Use
pwdandlsbefore executing - Test with `-i`: Use interactive mode if unsure about overwrites
- Use Tab Completion: Auto-fill names to prevent typos
- Check permissions: Ensure you have write access to the parent directory
- Avoid trailing slashes: Use
mv dir1 dir2notmv dir1/ dir2 - Metadata preservation:
mvmaintains permissions and timestamps
Warning: Avoid GUI drag-and-drop if preserving inode numbers/permissions is critical. CLI methods are more reliable for system directories.