Copying file paths as clickable links streamlines document sharing and navigation. Here's how to accomplish this efficiently on major operating systems.
Windows (Explorer)
- Method 1 (Address Bar):
Navigate to the file's folder. Click the address bar to reveal the full path. Select and copy (Ctrl+C). The path will be formatted like:
C:UsersNameDocuments* - Method 2 (Context Menu):
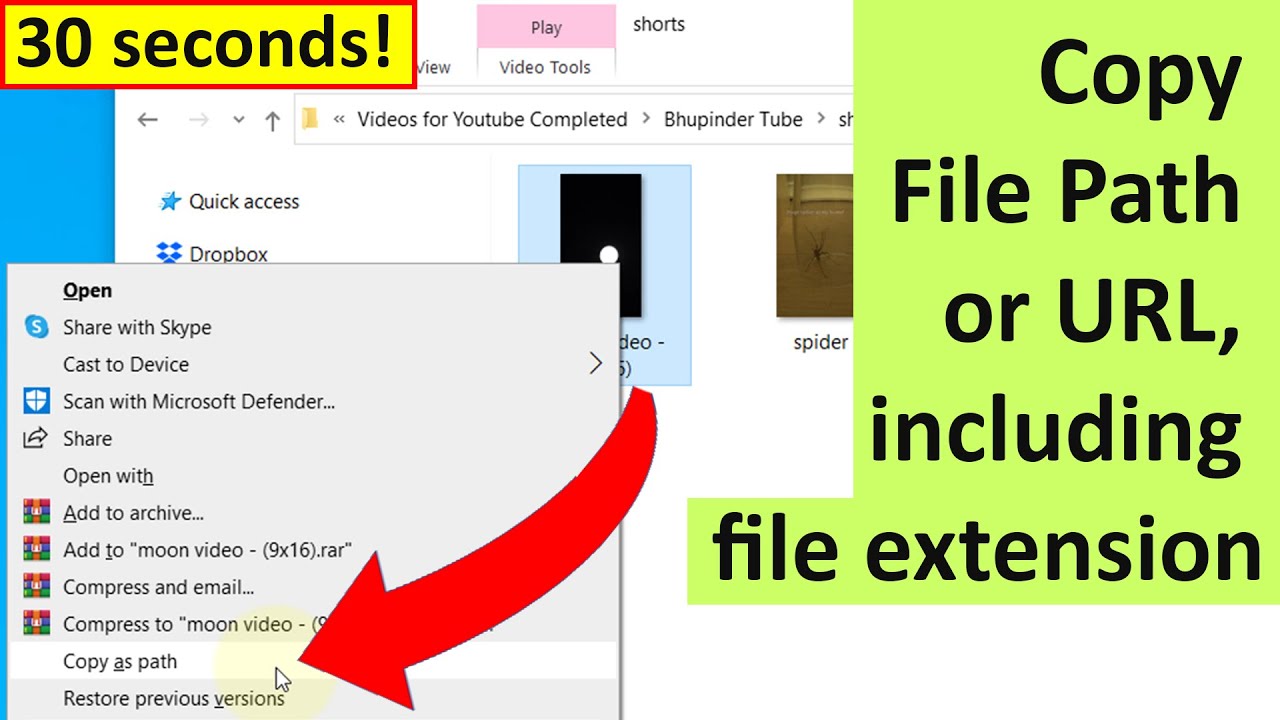
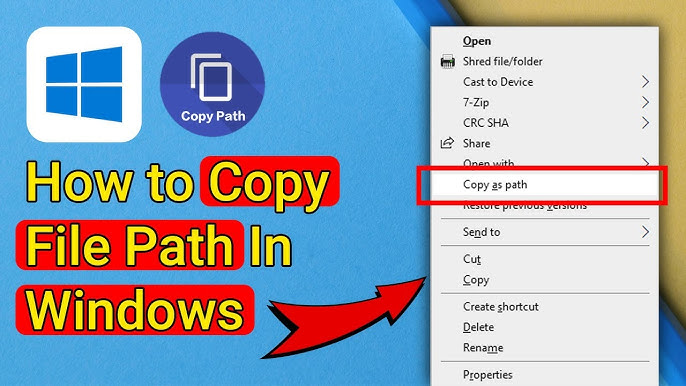
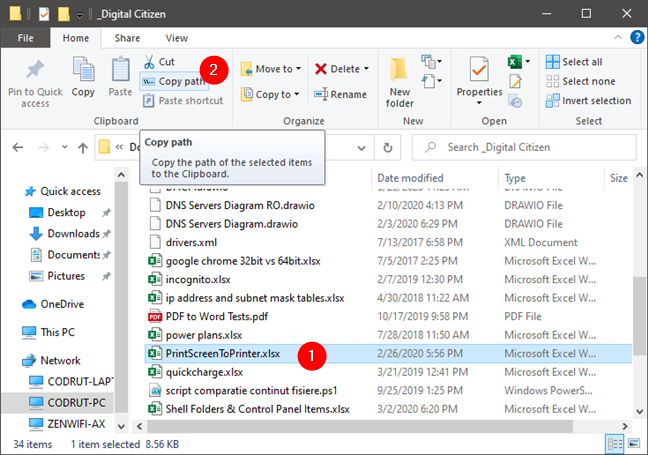
Select the file.

Hold Shift and right-click the file.
Choose "Copy as path" from the context menu.
macOS (Finder)
- Method 1 (Path Bar):
Enable the Path Bar: Go to View > Show Path Bar.
Select the file. The full path appears at the bottom.
Right-click (or Ctrl-click) the file's name within the Path Bar.
Select "Copy "[Filename]" as Pathname".
- Method 2 (Info Panel):
Select the file.
Press Cmd+I to open Info.
Find the "Where:" location. Click the small path text next to it once to highlight, then Cmd+C to copy.
Linux (Terminal)
Use the terminal for precise control.
- Find the Absolute Path:
Navigate to the file's directory using cd.
Type pwd (Print Working Directory) and press Enter.
This displays the current directory's full path (e.g., /home/user/Documents). Note this down.
- Construct the Full File Path:
Append a forward slash and the exact filename (including extension) to the directory path.
Example: /home/user/Documents/*
- Copy the Path:
Select the complete path string in your terminal.
Paste it (Ctrl+Shift+V or right-click paste in most terminals) where needed.
Important Notes
- Paths copied via "Copy as path" (Windows) or Path Bar (macOS) are ready for pasting into documents supporting links. Other methods paste the text path.
- Spaces in paths are handled automatically. Enclosing quotes may appear when pasting; they are valid for system use.
- If "Copy as path" isn't visible in Windows, ensure you hold Shift before right-clicking or check under "Show more options".