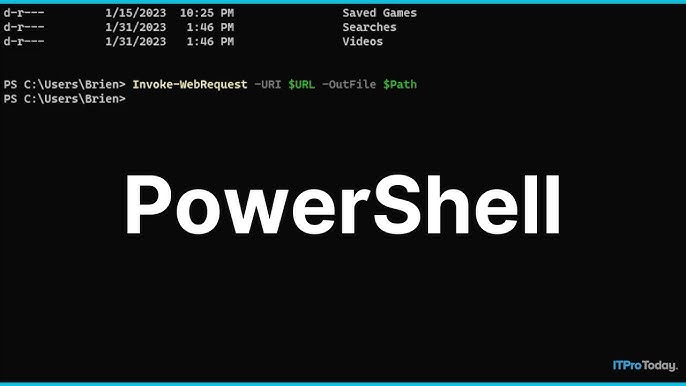
To download files using PowerShell, follow these step-by-step methods:
Method 1: Using Invoke-WebRequest (PowerShell 3.0+)
Basic Download:
- Execute:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "FileURI" -OutFile "C:Path*" - Replace
FileURIwith the file's full remote address. - Specify the local path and filename with
-OutFile.
Bypassing SSL/TLS Errors:
- Add
-SkipCertificateCheckbefore downloading if encountering certificate errors.
Handling Large Files:
- Use
-Resumeto support resuming interrupted downloads.
Method 2: Using * (Legacy Approach)
Simple Download:
- Execute:
(New-Object *).DownloadFile("FileURI", "C:Path*")
Async Download (Non-Blocking):
- Execute:
(New-Object *).DownloadFileAsync("FileURI", "C:Path*")
Method 3: Using Start-BitsTransfer (Efficient Transfer)
Basic BITS Transfer:
- Execute:
Start-BitsTransfer -Source "FileURI" -Destination "C:Path" - Add
-Asynchronousfor background transfers.
Resuming Transfers:

- Use
Get-BitsTransfer Resume-BitsTransferto restart paused jobs.
Essential Considerations
- Overwrite Files: Add
-PassThruto force overwrite existing files with Invoke-WebRequest. - Authentication: Use
-Credential (Get-Credential)with Invoke-WebRequest or-Authentication Basicwith Start-BitsTransfer for protected resources. - Headers: Include custom headers with
-Headers @{"HeaderName"="Value"}in Invoke-WebRequest. - User Agent: Specify UA string with
-UserAgent "AgentString"if required by server. - Progress Tracking: Utilize
$progressPreference = 'silentlyContinue'to suppress progress bars for scripting.
TLS 1.2 Enforcement (Older PS Versions): Add [*]::SecurityProtocol = [*]::Tls12 before download commands when targeting HTTPS endpoints requiring TLS 1.2.
REST API Authentication: For bearer tokens, use: Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "APIEndpoint" -Headers @{Authorization = "Bearer APIToken"} -OutFile OutputPath