What is BFD?
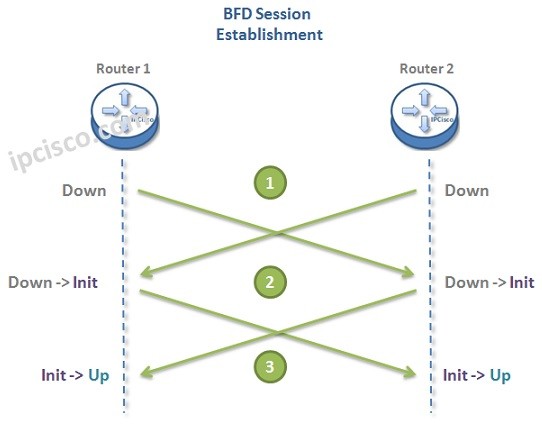
BFD stands for Bidirectional Forwarding Detection. It is a standardized network protocol (defined in RFC 5880) that quickly detects failures in the forwarding path between two devices, such as routers or switches. This enables rapid recovery mechanisms to maintain network availability.
How It Works
BFD operates by exchanging lightweight control packets between endpoints at configurable intervals (e.g., milliseconds). If a packet isn't received within the agreed timeout, BFD flags the path as down, triggering immediate rerouting without waiting for slower protocols like OSPF or BGP.
Key Advantages
- Ultra-Fast Detection: Achieves sub-second failure detection, often in 50ms or less, minimizing service disruptions.
- Low Resource Usage: Uses minimal bandwidth and CPU, making it scalable for large networks.
- Protocol-Agnostic: Integrates seamlessly with routing protocols like BGP, OSPF, or MPLS to accelerate convergence.
- Simple Implementation: Requires basic configuration but delivers high reliability for critical infrastructure.
Real-World Applications
BFD is essential for high-availability networks, such as those supporting VoIP, cloud services, and data centers. For example, it reduces downtime during link failures, ensuring continuous connectivity for enterprise and service provider environments.