Optimizing your GPU fan curve reduces noise while maintaining safe temperatures, extending component lifespan.
What is a GPU Fan Curve?
A fan curve maps GPU temperature to fan speed percentages, defining how aggressively fans spin at different thermal levels. Default curves prioritize cooling over quietness.
Why Optimize Your Fan Curve?
- Reduce Noise: Lower speeds at idle/moderate loads minimize acoustics without compromising cooling.
- Extend Fan Life: Less wear from constant high speeds.
- Improve Efficiency: Balanced airflow prevents thermal throttling or overheating.
Tools Required
Use software like MSI Afterburner, ASUS GPU Tweak, or similar applications. Ensure they are compatible with your GPU model for safe adjustments.
Step-by-Step Optimization Guide
- Monitor Baseline: Launch the tool and observe GPU temperatures and fan speeds under idle, gaming, and stress tests.
- Access Fan Curve Settings: Navigate to the fan control section. Enable user-defined curve mode.
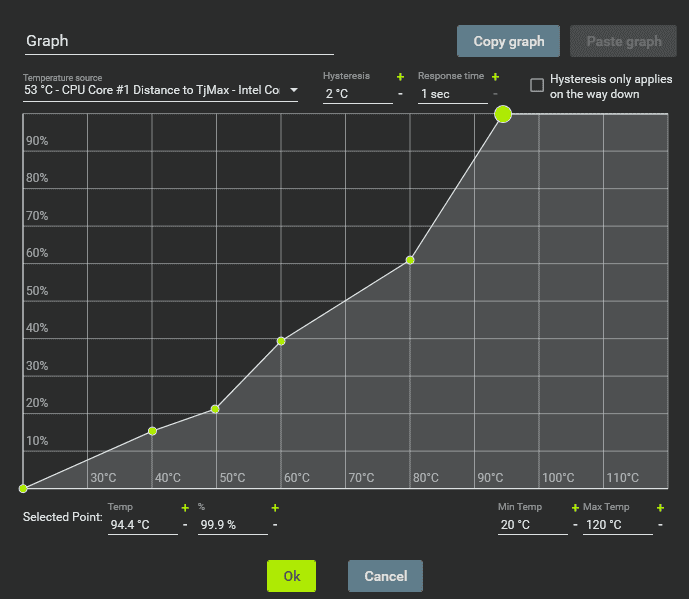
- Set Lower Idle Speeds: Adjust the curve so fans run at 20-30% (or the minimum audible level) below 50°C.
- Gradual Ramp-Up: Increase speed to 50-60% at 70°C, 70-80% at 80°C, and max at 90°C to prevent overheating.
- Test and Refine: Apply changes and run benchmarks. Monitor temps; if they exceed 85°C, raise speeds at critical points.
- Save Profile: Apply settings permanently to maintain optimizations.
Best Practices for Quieter Operation
- Avoid Steep Curves: Smooth transitions minimize fan noise spikes.
- Clean Regularly: Dust buildup forces fans to work harder; clean heatsinks every 3-6 months.
- Monitor Thermals: Keep max temps below 85°C during heavy use to ensure stability.
- Undervolt GPU: Combine with curve optimization to reduce heat generation and noise.
Safety Precautions
Never set fans below manufacturer minimums or disable them entirely. Test after each tweak; if instability occurs, reset to default.
Proper optimization yields significant noise reduction with negligible thermal impact.