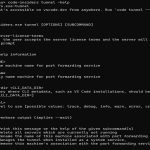
WPA2-AES is the foundational security protocol protecting most modern Wi-Fi networks. It combines the robust authentication framework of WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) with the strong AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) cipher for encrypting data.
Breaking Down WPA2-AES
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2): The successor to WPA and WEP. It significantly enhances security by mandating the use of the AES block cipher and introducing the CCMP (Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol). This provides both confidentiality and data integrity verification.
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): A highly secure symmetric encryption algorithm established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It encrypts the actual data transmitted over your wireless network.
How WPA2-AES Secures Your Connection
WPA2-AES operates via a four-way handshake when a device connects:
- A device requests connection to the password-protected network (PSK mode is most common for home users).
- The access point and device exchange messages to verify they both possess the correct Pre-Shared Key (PSK) – your Wi-Fi password.
- Successful authentication generates unique Pairwise Transient Keys (PTKs) for the session.
- Data transmission begins, encrypted using the AES algorithm and keys derived during the handshake.
CCMP wraps AES encryption, ensuring data confidentiality and detecting any tampering.

Why WPA2-AES is Important
- Strong Encryption: AES, particularly with 128-bit or longer keys (AES-128, AES-256), is computationally intensive to crack with current technology. It supersedes the weak and easily compromised WEP and the less secure TKIP protocol used in early WPA.
- Data Confidentiality: Prevents eavesdroppers from intercepting and reading data transmitted over your wireless network.
- Data Integrity: Protects against attackers modifying data packets in transit.
- Authentication: Ensures only authorized devices with the correct password can join the network.
Best Practices for Optimal Security
- Choose WPA2-AES: Always select "WPA2-Personal" (for home networks) or "WPA2-Enterprise" (using RADIUS servers) with "AES" encryption. Avoid options like "WPA/WPA2 Mixed Mode" or TKIP unless necessary for compatibility with very old devices.
- Use a Strong Password: The Pre-Shared Key (Wi-Fi password) is critical. Use a long, complex passphrase unique to your network. Weak passwords are vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- Keep Firmware Updated: Ensure your wireless router/access point and connected devices have the latest firmware to patch known vulnerabilities.