The mv Command Method
The fastest way to rename directories in Linux is using the mv command. Syntax:
mv /path/to/old_name /path/to/new_name
Execute this directly in your terminal. Example to rename a directory in the current location:
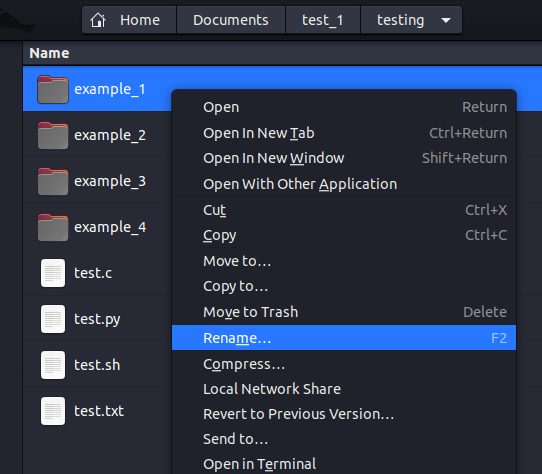
mv old_directory new_directory
Renaming with Absolute or Relative Paths
Specify full paths for directories outside your working location:
mv /home/user/docs /home/user/documents
Use relative paths for adjacent directories:
mv ../project_temp ../project_final
Handling Spaces in Names
Enclose directory names containing spaces or special characters in quotes:
mv "old project" new_project
Alternatively, escape spaces with backslashes:
mv old project new_project
Critical Safety Notes
- Overwrite Warning: If new_name exists, mv overwrites it silently. Verify target uniqueness first.
- Permissions: Ensure you have write access to the parent directory and the directory itself.
- Use Tab Completion: Press Tab after typing initial path characters to autocomplete names and reduce errors.
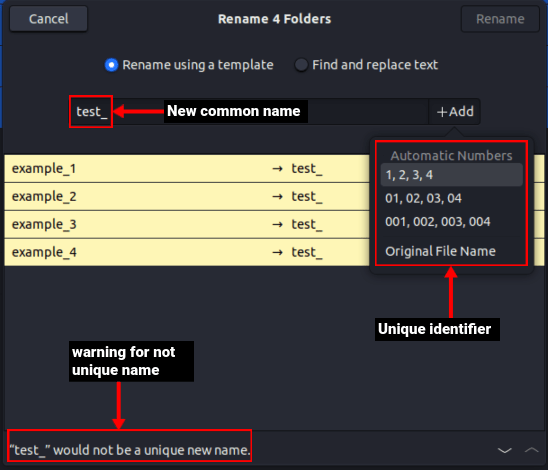
Batch Renaming Tip
For bulk renaming tasks, combine mv with loops or scripts. Example:

for dir in prefix_; do mv "$dir" "new_${dir#prefix_}"; done
This renames all directories starting with "prefix_" to "new_[original suffix]".