Prerequisites
Before converting, ensure your system meets these requirements to avoid data loss:
- Your disk uses the MBR partition style, and you aim to switch to GPT for UEFI booting.
- Back up all critical data using a reliable tool like external storage or imaging software.
- Verify that your hardware and firmware support UEFI boot mode; if not, conversion may cause boot failures.
- Ensure your operating system is Windows 10 version 1703 or later, or Linux with compatible tools like gdisk.
- The disk must have an active recovery partition and be connected directly to the system.
Conversion Steps Using * (Windows Focus)
Follow this procedure for a safe, data-preserving switch:
- Run Command Prompt as Administrator and execute: mbr2gpt /validate /disk:0 /allowFullOS to check compatibility.
- If validation passes, convert by running: mbr2gpt /convert /disk:0 /allowFullOS. This process modifies the partition table without altering data partitions.
- Restart your computer and access the UEFI firmware settings (typically by pressing F2 or Del during boot).
- In UEFI settings, disable legacy BIOS/CSM mode and enable UEFI boot, ensuring the GPT-formatted disk is set as the primary boot device.
Post-Conversion Verification
Confirm the switch was successful:
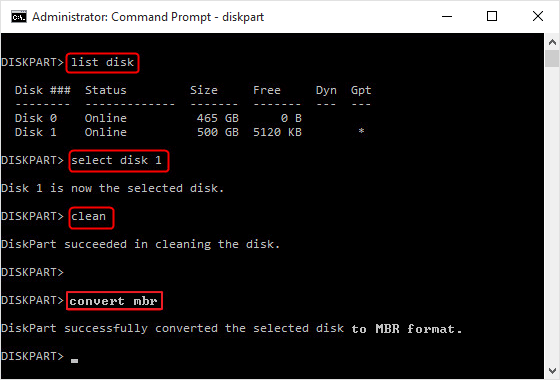
- In Windows, open Disk Management: if "GPT" appears under the disk properties, conversion worked.
- Boot into your OS normally; if successful, test applications and data access.
- If boot issues occur, use recovery media or boot repair tools to reconfigure the boot loader.
Note: If any step fails, revert to your backup immediately. For Linux systems, use gdisk to convert interactively, maintaining similar data-preserving steps.