Here are legitimate methods to launch Command Prompt (CMD) with administrative privileges without entering a password each time. Important: These techniques require you to already possess administrator credentials. They streamline access but do NOT bypass Windows security or crack passwords for unauthorized accounts.
Standard Methods (Password Required Initially)
These standard methods typically prompt for an admin password once per session via UAC:
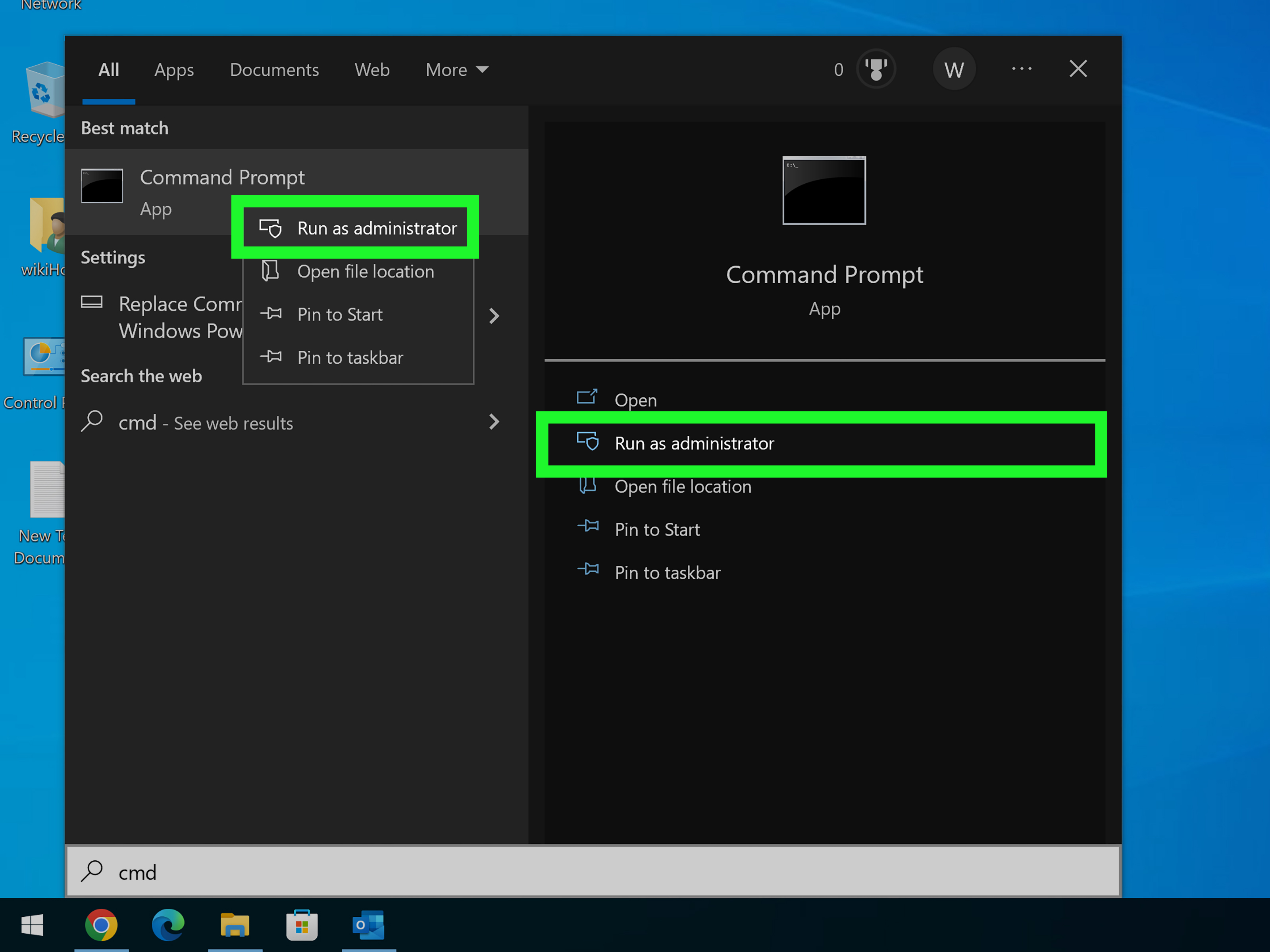
- Start Menu Search: Type "cmd", right-click "Command Prompt", select "Run as administrator". Enter admin credentials when UAC prompts.
- File Explorer Path: Navigate to
C:WindowsSystem32, find "*", right-click it, select "Run as administrator". Enter admin credentials. - Run Dialog: Press Win+R, type
cmd, then press Ctrl+Shift+Enter simultaneously. Enter admin credentials when UAC prompts. - Task Manager: Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc, go to "File" > "Run new task". Type
cmd, check the "Create this task with administrative privileges" box. Enter admin credentials if prompted.
Methods Avoiding Repeated Password Prompts (Initial Setup May Be Needed)
These methods aim to prevent needing the password every single time after initial setup or in specific contexts:
- Use an Elevated Administrator Account: If you log into Windows using a local Administrator account (often called "Administrator"), UAC prompts for standard tasks are disabled by default. Running CMD from this session doesn't require an additional password. Warning: Running constantly as a full Administrator is a security risk.
- Enable Built-in Administrator Account (Requires Initial Setup): Enable the hidden built-in Administrator account, which has elevated privileges without additional prompts (after initial login). Requires administrative rights initially:
- Run CMD as admin once (using password).
- Type:
net user Administrator /active:yesand press Enter. Set a password if required. - Log out and log in as "Administrator". Launching CMD from this session won't prompt again.
- Runas Command with Saved Credentials (Not Recommended):
- Run CMD as admin once (using password).
- Type:
runas /savecred /user:Administrator "*"(replace "Administrator" with your admin username). Enter password. - Future Use: Running
runas /savecred /user:Administrator "*"will launch admin CMD without prompting. Major Security Risk: Credentials are stored weakly. Not advised.
- Create a Shortcut with Advanced Properties (For Standard User Accounts):
- Right-click Desktop -> New -> Shortcut.
- Location: -> Next -> Name it (e.g., "Admin CMD") -> Finish.
- Right-click the new shortcut -> Properties.
- Click "Advanced..." -> Check "Run as administrator" -> OK -> Apply/OK.
- Double-clicking this shortcut triggers a UAC prompt. Enter the admin password once per session. Subsequent uses of this shortcut in the same Windows session usually won't re-prompt (unless credentials changed).
- Windows Terminal (Windows 10/11): Install Windows Terminal from the Microsoft Store. Open its settings (Ctrl+,). Edit your Command Prompt profile () to add:
"elevate": trueOR"elevateIfAdmin": trueThis will attempt to launch CMD elevated when started from Terminal. You'll get a UAC prompt asking for the admin password initially.
Critical Considerations
- Security: Methods avoiding repeated UAC prompts (especially runas /savecred and constant Administrator login) significantly reduce system security. Only use them on trusted, secure machines if absolutely necessary.
- UAC is Your Friend: UAC prompts protect your system. Disabling or heavily circumventing them is not recommended for daily use.
- Policy Restrictions: These methods require standard privileges. If Group Policy strictly prevents privilege escalation, only a domain administrator can change them.












